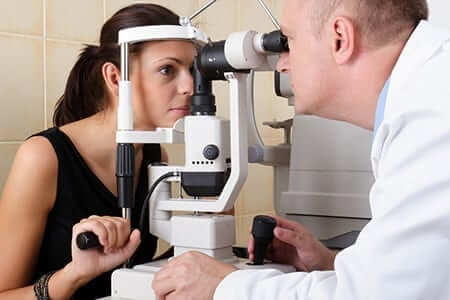
People with diabetes should schedule regular yearly visits to an ophthalmologist/optometrist to avoid eye problems. High blood sugars from diabetes can increase the risk of eye problems. Discover why it is essential to include an eye doctor as part of your diabetes health care team.
- High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of eye problems from diabetes. For adults aged 20 to 74, diabetes is the leading cause of blindness. You should monitor your blood sugar levels regularly by using a glucose monitor. Record the results and share them with your physician during regular visits. Report any extreme highs or lows to your doctor right away.
- If your vision is blurry, it could be a temporary problem caused by high blood sugar levels. This causes the lens of the eye to swell and changes your ability to see. To correct this problem, get your blood sugar back in the target range. The ideal range is 80-120 mg/DL prior to meals and between 140- 180 mg/DL two hours after a meal. It can take up to three months after you achieve blood sugar control to minimize blurriness and get your vision back to normal. Discuss blurred vision with your doctor immediately as it could be a symptom of serious eye problems associated with diabetes such as cataracts, glaucoma and retinopathy. Never get your eye glass prescription changed while your blood sugars are elevated and your vision is blurry.
- Cataracts is a cloudiness of the clear lens of the eye. This can impair your vision by causing an inability to focus light. This leads to glared or blurred vision. Cataract surgery may be done to remove or clean out the cloudy lens and replace it with a clear man-made one. Have your eye doctor check for cataracts during routine exams.
- Pressure forms inside the eye when the fluid does not drain properly. This eye problem is called glaucoma. The pressure may damage blood vessels and nerves in the eye causing changes in vision. The most common form of glaucoma, open-angle glaucoma, requires lowering the pressure in the eye. This can be done with medication, special eye drops, laser procedures or surgery to improve the eye’s aqueous drainage. There could be no symptoms until the disease is advanced and causes vision loss. Some symptoms may include eye aches, blurry vision, headaches, and halos around lights, watery eyes and loss of vision. Schedule an annual glaucoma screening from your eye doctor to detect this problem as soon as possible.
- People with diabetes are more prone to getting neo-vascular glaucoma, an uncommon form of this disease. The blood vessels grow in the iris, the colored part of your eye, which blocks the normal flow of fluid out of your eye. This raises eye pressure. Treatment is difficult and may include laser surgery to reduce the vessels.
- Diabetic retinopathy occurs due to damage of small blood vessels in your eyes. Improving your blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol control, can reduce your risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. Blood sugar control may include the use of oral medications, the use of an insulin pump or multiple daily injections of insulin. Types of diabetic retinopathy include background retinopathy, maculopathy and proliferative retinopathy. Try to reduce risk factors that can worsen occluded vessels. Quit smoking, reduce your cholesterol, exercise regularly, and have good blood sugar control. Treatment of diabetic retinopathy may include laser surgery. Have your doctor screen your eyes annually for diabetic retinopathy.
- Schedule an eye exam at least once a year. If you have new problems, contact your eye doctor right away. Symptoms of eye problems may include flashes of light, blurred vision, black spots, floaters or holes in your vision. Maintain proper blood sugar control by exercising at least 30 minutes a day and eating a healthy diet with fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy items, lean meats, fish and poultry and whole grain. Take medications as prescribed by your doctor.
With proper blood sugar control and healthy lifestyle habits, you can reduce the risk of developing eye problems associated with diabetes. Schedule an annual eye exam that includes testing for cataracts, glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy. If you experience any vision problems between routine exams, contact your eye doctor immediately.










Leave A Comment