Almost 20 percent of Americans over the age of 65 have diabetes and another quarter of the older population have insulin resistance. Diabetes diagnosis and treatment can be challenging for the elderly, especially when the annual out-of-pocket costs can be up to $12,000. Find out more about how diabetes affects the elderly and what to do about it.
- As people get older, it is more common to develop diabetes and it can become more difficult to diagnose the symptoms. Warning signs include frequent urination, blurry vision, fatigue and increased thirst. These symptoms may also be associated with aging but should never be ignored. Other symptoms of diabetes could include incontinence and mental confusion. Immediately report any of these symptoms to the person’s health care provider.
- Be aware of the symptoms of hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar. This often occurs when an elderly person with diabetes misses a meal or snack. Symptoms include cold and clammy skin, fatigue, irritability, hunger and confusion as well as trembling, stomach pain, dizziness or headache. Hypoglycemia may lead to fainting and even unconsciousness. Immediately give the person something with sugar that is easily and quickly absorbed into the system such as glucose tablets, regular soda or juice.
- High blood sugar, also called hyperglycemia, typically happens when an elderly person eats too much, misses their medication or fails to exercise. It can also be triggered if the person has an infection or has another illness. Common symptoms include fatigue, thirstiness, frequent urination and confusion as well as agitation and high levels of ketones in the urine. The person might also experience weight loss. If an elderly person has these symptoms, immediately contact the doctor or call for emergency care.
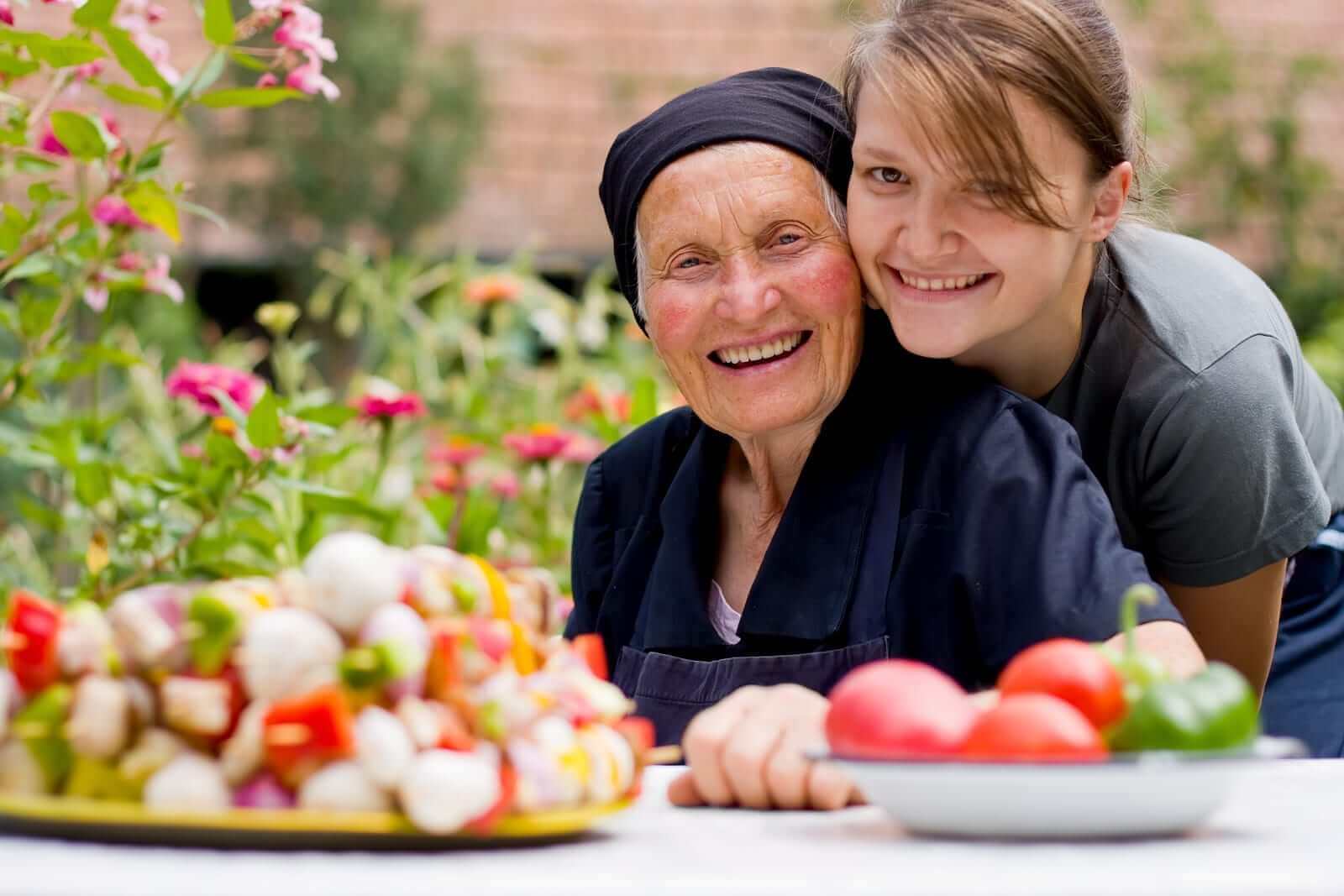
- Depression, mental illness and dementia are other complications an elderly person may experience. These issues can make it more difficult to effectively treat diabetes. The person might miss meal times, fail to check blood sugar levels or forget to take prescribed medication. A person with these conditions might need a caregiver or home health aide to ensure they are properly cared for.
- Financial limitations are another issue faced by many elderly people with diabetes. The cost of medication may exceed their budget. It could be hard for them to get transportation to and from necessary medical appointments. They might get little exercise and suffer from poor nutrition. Take advantage of Medicare and other federal programs to get an older person the help they need. Carefully review the person’s insurance coverage to get the maximum benefits. Inquire about medical transportation programs through local community centers and houses of worship. Supplement meals with vitamins. Consider a service such as Meals on Wheels to ensure the person gets meals delivered regularly. Many Medicare Advantage programs offer gym memberships, free transportation and prepared delivered meals.
- Give elderly people with diabetes the tools to succeed. A medication manager can help a person remember to take insulin and other medications at the proper times. Remind the person to use glucose meters to check blood sugars. Keep plenty of supplies on hand. Help the person get daily exercise. Treat complications right away. Work with a medical health care team to ensure the person gets appropriate care. These professionals may include a diabetic nurse, home health care aide and nutritionist as well as a personal trainer and various doctors such an endocrinologist and podiatrist. Remember to schedule annual eye exams and dental visits twice a year.
- Verify the elderly person bathes regularly and maintains proper oral hygiene. Modify the bathtub with handles, seats and other helpful devices if the person has trouble getting into and out of the shower. Encourage the person to use moisturizer to combat dry skin. Check the person’s feet regularly for cuts, blisters, callouses or other issues. Make sure their toenails are properly clipped. Take the person to a podiatrist to get the job done right which is covered by Medicare.
- Stock the kitchen with healthy foods that are simple to prepare. Elderly people with diabetes should eat whole grains, low fat dairy and plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. They should also eat lean meats and fish. Have diabetic snacks on hand as a treats. Keep sugary, salty and pre-prepared foods out of the pantry as they can lead to health complications.
- Verify certain tests are done each year. Have the person’s kidneys checked. Make sure they get a blood test at least once a year to check cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Get an A1C test per physician’s guidelines to show the person’s average 3 month glucose level. Schedule a yearly flu shot. People over 65 should also get the pneumonia vaccine.
It is crucial for elderly people with diabetes to be well-prepared for emergencies. Keep plenty of supplies on hand and work with a team of health care professionals. Take advantage of insurance coverage and governmental programs to help elderly people get the medications, food and health care they need.











Leave A Comment