It seems there are a tremendous number of medication choices available to manage the condition of diabetes. The goal of these medications is to keep your blood glucose levels within your personal target range set by your physician or diabetes educator, as well as the guidelines set by the American Diabetes Association. The physician will decide which medications to use based on the type of diabetes you have, your life style, your kidney and liver function, as well as your other health conditions.
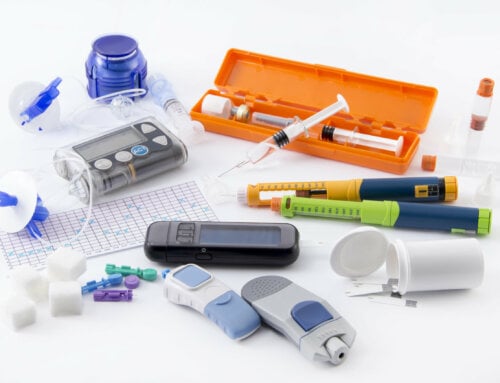
Injections – Insulin and other injectables are delivered through insulin needles and syringes or pen delivery systems.
-
- Insulin. Insulin is prescribed for people with diabetes who do not produce any insulin, enough insulin, or whose bodies do not use insulin correctly, as in insulin resistance. Types of insulin vary according to how quickly they start working (onset), the time at which the insulin works at maximum strength (peak time), and how long it continues to lower blood glucose (duration). Your physician will prescribe the insulin based on multiple factors. Here is a list of the available types of insulin.
| Name | Type | Onset | Peak | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apidra/Humolog/Novolog | Rapid-acting | 10 – 15 min | 1 – 1.5 hrs | 2 – 4 hrs |
| Humulin/Novolin [Velosulin is for pumps] | Regular (short-acting) | 30 – 60 min | 2 – 5 hrs | 5 – 8 hrs |
| NPH | Intermediate-acting | 2 – 4 hrs | 4 – 12 hrs | 12 – 18 hrs |
| Levemir/Lantus | Basal | 1 hr | No real peak | 20 – 24 hrs |
| Humulin 70/30 | premixed | 30 min | 2 – 4 hrs | 14 – 24 hrs |
| Novolin 70/30 | premixed | 30 min | 2 – 12 hrs | Up to 24 hrs |
| Novolog 70/30 / Humolog 70/30 | premixed | 10 – 20 min | 1 – 4 hrs | Up to 24 hrs |
| Humulin 50/50 | premixed | 30 min | 2 – 5 hrs | 18 – 24 hrs |
| Humolog 75/25 | premixed | 15 min | 30 min – 2.5 hrs | 16 – 20 hrs |
- Other injectables. Two other injectables can be used to treat diabetes. Pramlintide or Symlin is a synthetic form of amylin, [amylin analog] a hormone produced by the pancreas (where insulin is also produced). Symlin helps maintain normal blood glucose levels over the long term; Symlin is prescribed for people already on insulin and taken prior to meals with insulin. It may assist in weight loss and decrease hunger. It is only available in pens and can increase the risk of hypoglycemia. Exenatide or Byetta, another type of injectable, only available in pre set pens, increases insulin secretion to help lower blood glucose levels. It can be given along with oral agents. Byetta is taken twice daily, within an hour of meals. These injectables slow gastric emptying, decrease hunger and aid in weight loss. Victoza is taken only once daily in a pre set pen. Byetta and Victoza are GLP1 analogs.
Pill Medications for Diabetes: The Basics
Pills – There are six main classes of oral medications that people with diabetes may take as part of their treatment routine.
Sulfonylureas and meglitinides help the pancreas release more insulin. The sulfonylureas include Glipizide, Glyburide, and Glimepiride. They can increase your risk of hypoglycemia and weight gain. The meglitinides are shorter acting and are taken 10 minutes before eating meals. Their major effect is on post prandial blood sugars. They include Prandin or Starlix.
- Biguanides cause the liver to produce less glucose. Metformin, the main brand, also helps sensitize muscle tissue to blood glucose, which allows more glucose to be absorbed. Other names include Glumetza, Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Riomet or Fortamet.
- Alpha-Glycosidase Inhibitors prevent some starches (like bread and pasta) from breaking down. This helps keep blood glucose levels lower; these medications also cause some sugars to break down more slowly. They can increase the chance of gas, bloating, cramps, or diarrhea. This includes Precose and Glyset.
- Thiazolidinediones reduce glucose production in the liver. In addition, these drugs sensitize fat and muscle to accept insulin more easily and reduce insulin resistance. Actos and Avandia are included in this category. Avandia has recently been restricted because of increased risk of cardiac complications, increased liver enzymes and fluid retention. Actos is also being looked at carefully for complications as well.
DPP-4 Inhibitors help GLP-1 do its job. GLP-1 is a natural compound found in the body that reduces blood glucose levels. Unfortunately, GLP-1 is quickly broken down by DPP-4, an enzyme. As the name suggests, DPP-4 inhibitors block this enzyme from breaking down GLP-1. Included are Januvia, Onglyza, and Tradjenta. These medications do not cause weight gain and may be taken with other oral medications.
Many of the oral medications listed here can be taken in combination to give a better overall result in controlling blood glucose.
If you are taking one or more medicines for diabetes, it’s always a good idea to arm yourself with knowledge. Do some research on how your medication works, and talk with your doctor or pharmacist if you have any question; make sure you take the medication as directed and always mention any problems to your physician.




Leave A Comment